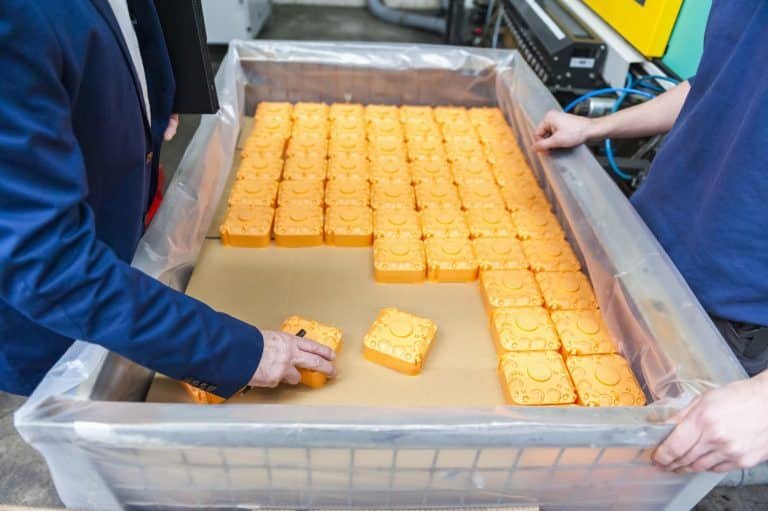
Injection molding, a manufacturing process of unparalleled importance, has revolutionized the production of plastic components across industries. From intricate medical devices to everyday consumer goods, the stability of injection molded finished products is a linchpin in ensuring reliability, functionality, and consistency. This introduction aims to dissect the key components that collectively contribute to the stability of injection molded products, presenting a point-by-point exploration of the intricate factors governing their quality.
1. Material Selection: The Genesis of Stability
Melting Temperature: The starting point in achieving stability lies in selecting a material with an optimal melting temperature. This crucial parameter ensures that the material can be effectively transformed from a solid to molten state during the injection molding process, laying the foundation for successful molding.
Flowability: The ease with which molten plastic flows within the mold is determined by factors like Melt Flow Index (MFI) or Melt Mass Flow Rate (MFR). A judicious choice of material with appropriate flow properties ensures that intricate details are faithfully replicated in the finished product, contributing to its stability.
Shrinkage: Understanding and managing shrinkage is imperative for maintaining dimensional stability. By selecting materials with predictable shrinkage characteristics, manufacturers can compensate for the natural contraction that occurs during the cooling phase, preventing deviations from design specifications.
Mechanical Properties: Tensile strength, flexural strength, and impact resistance are pivotal mechanical properties that influence the functionality and durability of the finished product. Tailoring material selection to match the mechanical demands of the application enhances the stability and performance of injection molded products.
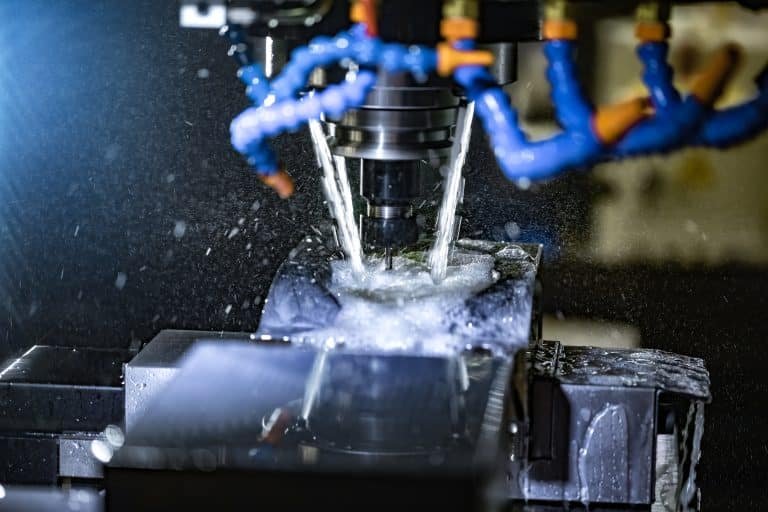
2. Process Optimization: Precision at Every Stage
Temperature Control:
The injection molding process involves a delicate balance of temperatures, from melting the raw material to cooling the molded product. Maintaining precise temperature control throughout ensures consistent material behavior, minimizing defects and enhancing product stability.
Injection Pressure and Speed:
Mold filling is critical, requiring precise calibration of injection pressure and speed to prevent defects like flash or incomplete filling, thus ensuring process stability.
Cooling Rates:
Controlled cooling rates play a pivotal role in influencing the material’s crystallinity and, consequently, its mechanical properties. Careful cooling minimizes warping risk and preserves the material’s intended shape, improving the finished product’s stability.
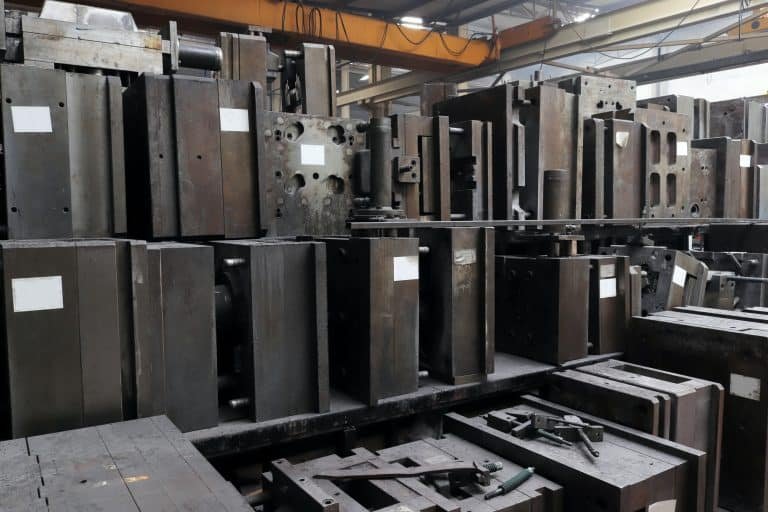
Mold Design and Maintenance:
The design and maintenance of the mold are integral aspects of process optimization. A well-designed mold, maintained regularly, reduces defects and inconsistencies, crucially stabilizing the injection molding process.
3. Quality Assurance: Safeguarding Stability
Testing and Inspection Protocols:
Robust testing and inspection protocols are essential to identify deviations from specifications early in the process. Dimensional checks, visual inspections, and non-destructive tests verify product adherence to standards, enhancing finished product stability.
Traceability:
Thoroughly documenting material batches, process parameters, and production data facilitates swift issue identification and resolution. Traceability is a key factor in enhancing the stability and consistency of the manufacturing process.
Employee Training and SOP Adherence:
Skilled and knowledgeable operators contribute to the precision and repeatability of the injection molding process.
Employee training and adherence to standardized procedures are key to quality assurance, guaranteeing stability in finished product production.
In summary, the stability of injection molded products hinges on meticulous material selection, process refinement, and quality assurance measures. Each point in this exploration represents a crucial facet in the pursuit of high-quality, consistent, and reliable products. As industries increasingly turn to injection molding for mass production, prioritizing stability drives innovation, efficiency, and excellence in manufacturing.