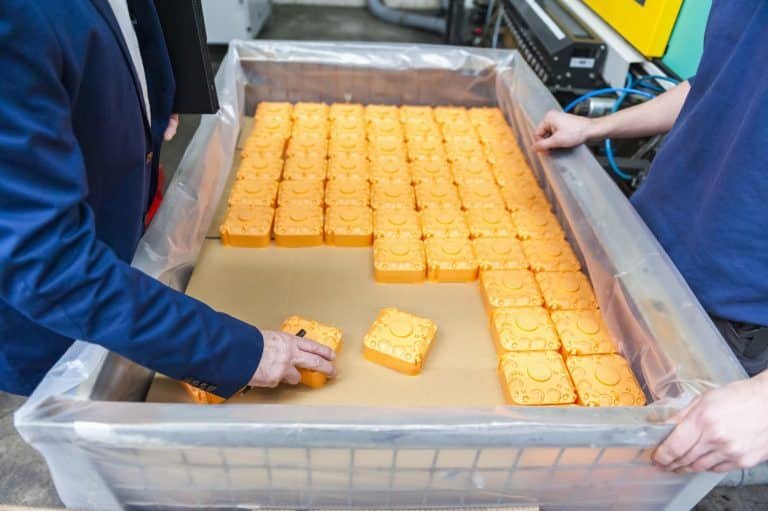
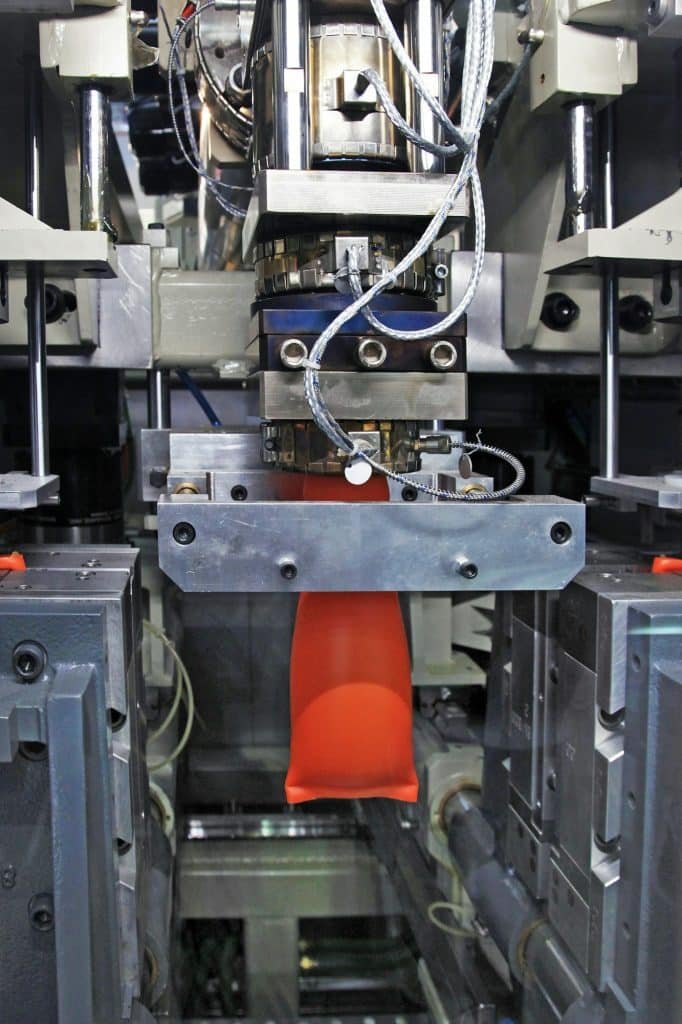
In the case of increasingly fierce competition in injection molding, improving production efficiency is a problem worthy of attention. Here is how to improve the injection cycle.
The injection cycle of an oil pressure-driven injection molding machine refers to the period from the beginning of the mold closing to the next mold closing. Mold closing is generally divided into four sections: fast mold closing, slow mold closing, low-pressure mold protection, and high-pressure mold locking. Injection begins after high-pressure mode-locking is completed and is divided into multiple stages. The mold cavity is filled with molten plastic during injection. When the mold cavity is filled, the pressure rises, and the end control of the infusion is inappropriate, the finished product will produce a rough edge.
Pressure retention begins after the injection is complete. Cooling begins after the mold cavity is filled, that is, it starts from the pressure preservation. When the mold cools, the finished product shrinks. The role of holding pressure is to fill the depression formed by shrinkage through the cold flow channel that has not yet solidified, and the holding pressure is generally lower than the injection pressure so that the finished product is full when de-molding (without dents). When the cold flow path solidifies, the pressure holding can be terminated. The pressure holding can be divided into multiple sections, and the pressure holding pressure of each section is different (generally decreasing step by step), which is divided by time.
The total holding time is set by the finished weight or dent. Adjust from a short holding time, and increase the holding time a little for each injection molding, until the weight of the finished product no longer increases or the production dent is acceptable, the holding time does not need to be increased.
Many thin-walled products do not need to hold pressure because the inner layer of the finished product is solidified immediately after injection.

The cooling time parameter set by the injection molding machine is a period from the completion of the pressure holding to the opening of the mold, but the cooling begins as early as the mold cavity is filled with plastic. The purpose of the cooling time is to allow the finished product to continue to cool and solidify, without deformation due to ejection. It should be said that the cooling time is based on experiments. In the beginning, the storage is carried out simultaneously. The cooling time is longer than the storage time, or the storage time may be longer than the cooling time. If the storage time is longer than the cooling time, it indicates that the plasticizing capacity of the screw is insufficient, which affects the production cycle.
Therefore, increasing the plasticizing capacity is the way to shorten the cycle time in this case, and the goal is to shorten the storage time.
The finished product is pushed out once or many times, the thimble will be closed again, and the next cycle begins immediately, the newly designed elbow injection molding machine has a regenerative closing oil path (differential closing function), to strive for higher closing speed, under the premise of the mold is not affected by high impact, suitable for use. High voltage clamping adopts the lowest clamping force that can make the finished product not produce burring, which can shorten the time required for a high voltage clamping section.
Molds, injection molding machine rods, toggle joints, and formwork will also extend their life due to low clamping forces. High injection rates can be used in the injection section if the finished product does not produce defects such as bubbles or burning. The use of the lowest injection pressure reduces the required clamping force (expansion force), while the use of the lowest barrel temperature reduces the cooling time.

The cooling time is related to the efficiency of the heat exchange of the mold, and the design of the appropriate mold can improve the efficiency of the heat exchange. However, where permitted, ice water cooling can shorten the cooling time. The ice water cooling causes the mold to condense, and the dry fan and the sealed mold locking device can reduce the dew point and prevent condensation.
If the plasticizing capacity is not enough to affect the production cycle, the following can be done in the screw design and parameter adjustment:
a: The screen screw can increase the plasticizing ability.
b: Large-diameter screws can increase plasticizing capacity.
c: Increasing the groove depth of the screw can increase the plasticizing capacity.
d: Increasing the speed of the screw can increase the plasticizing ability (certain shear-sensitive plastics such as PVC, PET, etc., cannot use this method).
e: Reducing the back pressure as much as possible will increase the plasticizing speed.
f: The oil pressure sealing nozzle is used to plasticize the mold when opening and closing.
g: The use of a pre-plasticizer design can make the screw plasticized in the cycle except for injection and pressure holding time.
h: The use of a pressure holding device, so that the screw in the pressure holding section can also plasticize.
The backup cable (ejection) before and after feeding is time-consuming and should be replaced by a spring nozzle or oil pressure seal, eliminating the backup cable action. The mold is opened at the highest speed without tearing the finished product and producing a large opening noise. Some injection molding machines have decompression equipment before opening the mold, and high-speed opening of the mold will not produce sound.
To achieve an accurate stop position at the high-speed opening, a brake valve or closed-loop control can be used. In the small injection molding machine with a small ejection force, the pneumatic ejection can be used, which is higher than the oil pressure ejection speed. Electric ejection is faster than pneumatic ejection. Using independent oil, gas, or circuit control, it can realize the function of multiple ejection side opening die side ejection.
Several ejections of some finished products can be vibratory ejections of injection molding machines. The thimble does not need to be fully withdrawn each time to shorten the time of multiple ejections. The final ejection may begin at the same time as the closing. Because the travel of the thimble is relatively short, the thimble is always fully backward before the mold is locked.