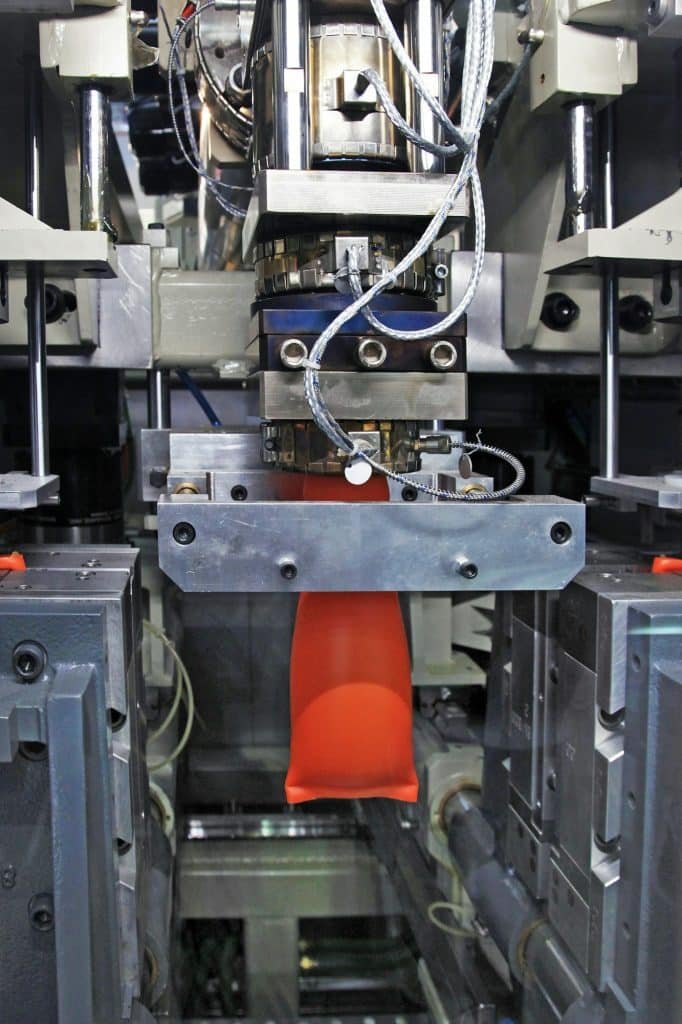
In the vast landscape of modern manufacturing, the Injection Molding process stands as a cornerstone, revolutionizing the production of intricate plastic components used in a myriad of industries. This highly versatile and efficient technique involves a series of meticulously orchestrated steps, seamlessly transforming raw plastic materials into precise and complex forms.
I. Overview of Injection Molding
Introduction to Injection Molding:
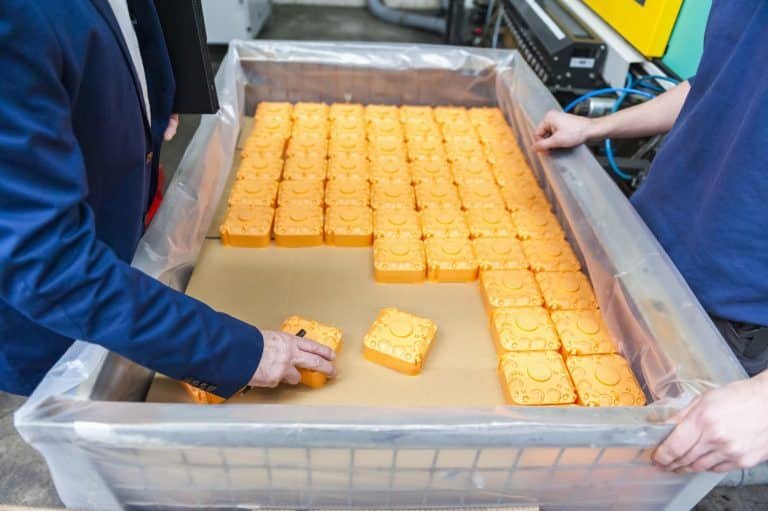
Injection Molding is a manufacturing process that involves the injection of molten plastic material into a mold cavity, allowing it to cool and solidify, ultimately taking the shape of the desired product.
This process is widely employed for the production of a diverse range of items, from small and intricate components to larger, more complex structures.
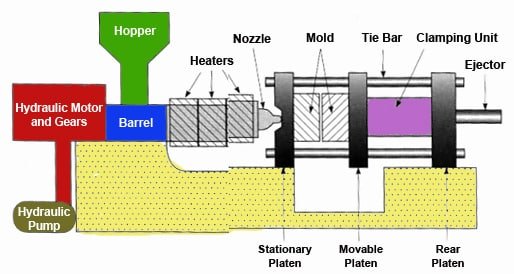
Basic Components of the Injection Molding Machine:
Hopper: Raw plastic material is fed into the machine through the hopper.
Barrel: Within the barrel, the plastic material is heated to a molten state.
Screw or Plunger: The molten plastic is then injected into the mold cavity using a screw or plunger mechanism.
Source: www.sciencedirect.com
II. The Injection Molding Process Unveiled
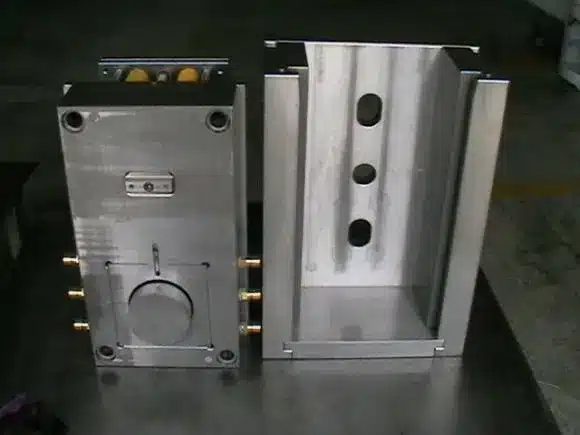
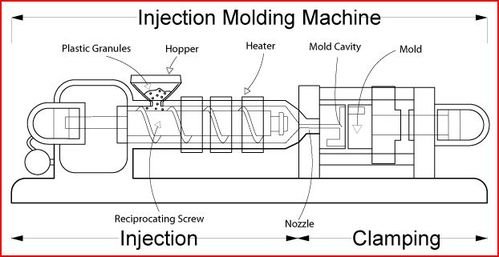
Clamping:
The first step involves closing the mold, creating a sealed cavity for the molten plastic to be injected into.
The clamping unit ensures that the mold remains closed with adequate force during the injection and cooling phases.
Source: www.plasticsmanufacuringsystems.weebly.com
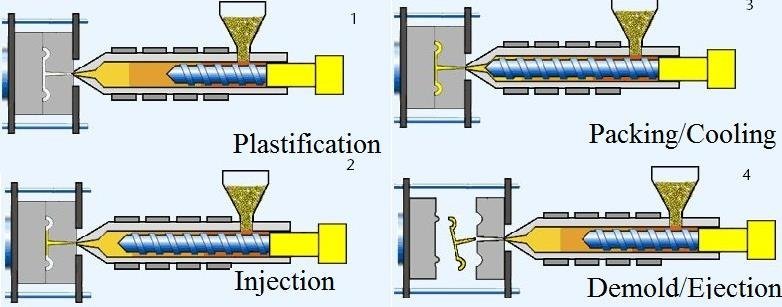
Injection:
The molten plastic material is injected into the mold cavity at high pressure through the nozzle.
The injection phase requires precision to fill the mold completely and avoid any defects.
Source: www.researchgate.net
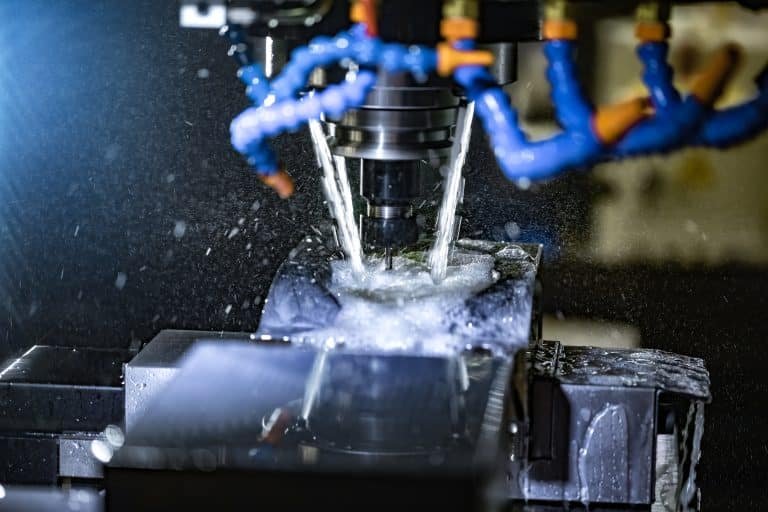
Cooling:
Once the mold is filled, the cooling phase begins. The molten plastic solidifies and takes the shape of the mold.
The cooling time is crucial in determining the final quality of the product.
III. Post-Injection Steps and Quality Assurance
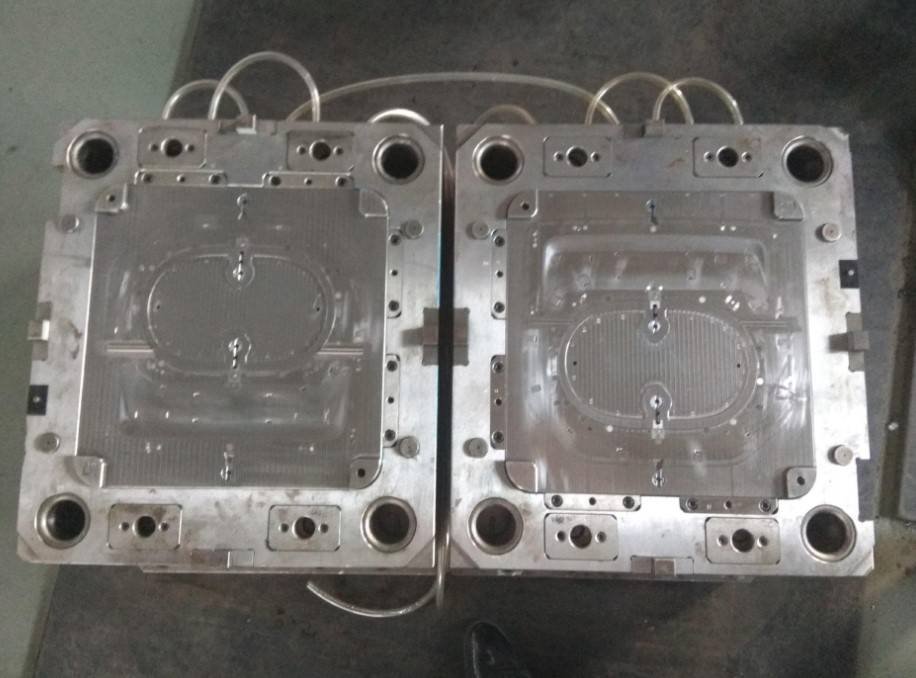
Opening the Mold:
After the cooling phase, the mold is opened, revealing the newly formed plastic product.
The ejection system assists in pushing the product out of the mold.
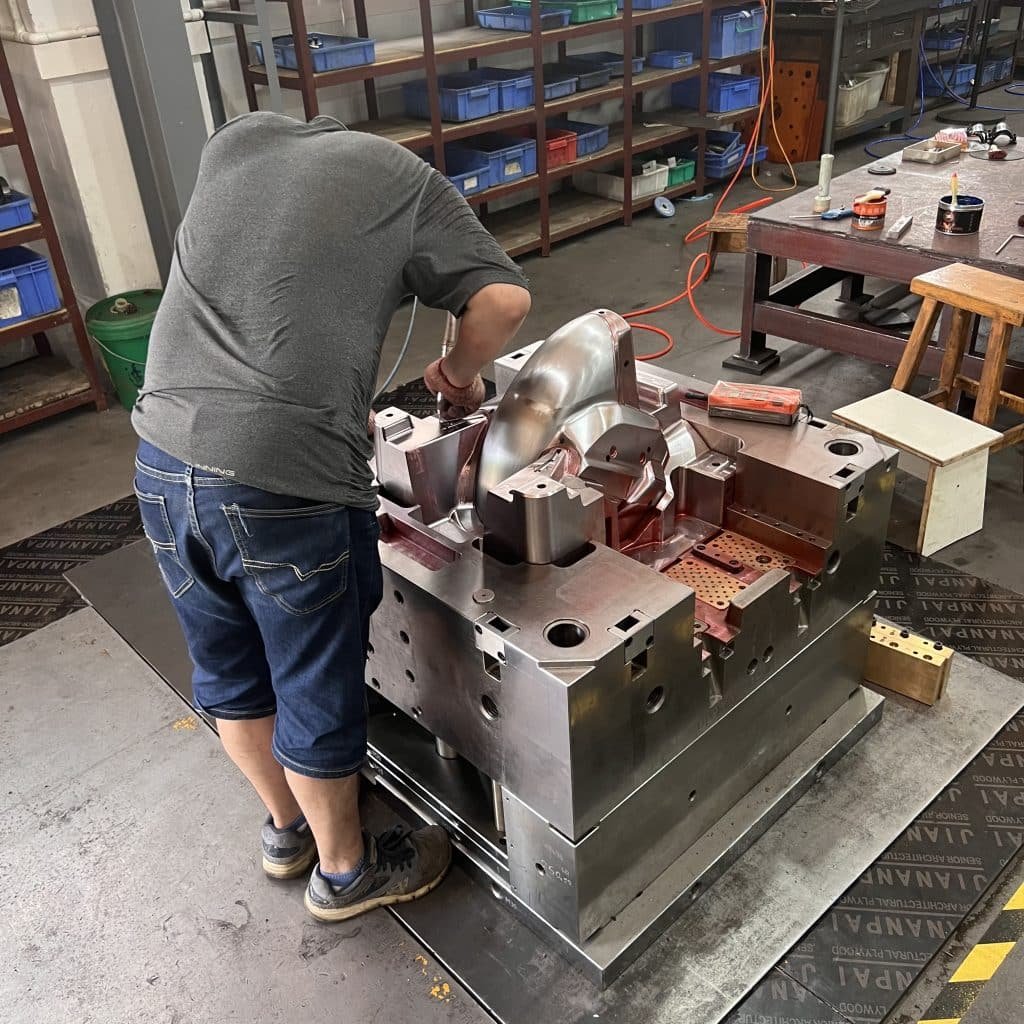
Trimming and Finishing:
Excess material, known as flash, is trimmed off to ensure the final product meets specifications.
Any additional finishing processes, such as painting or assembly, may be performed at this stage.
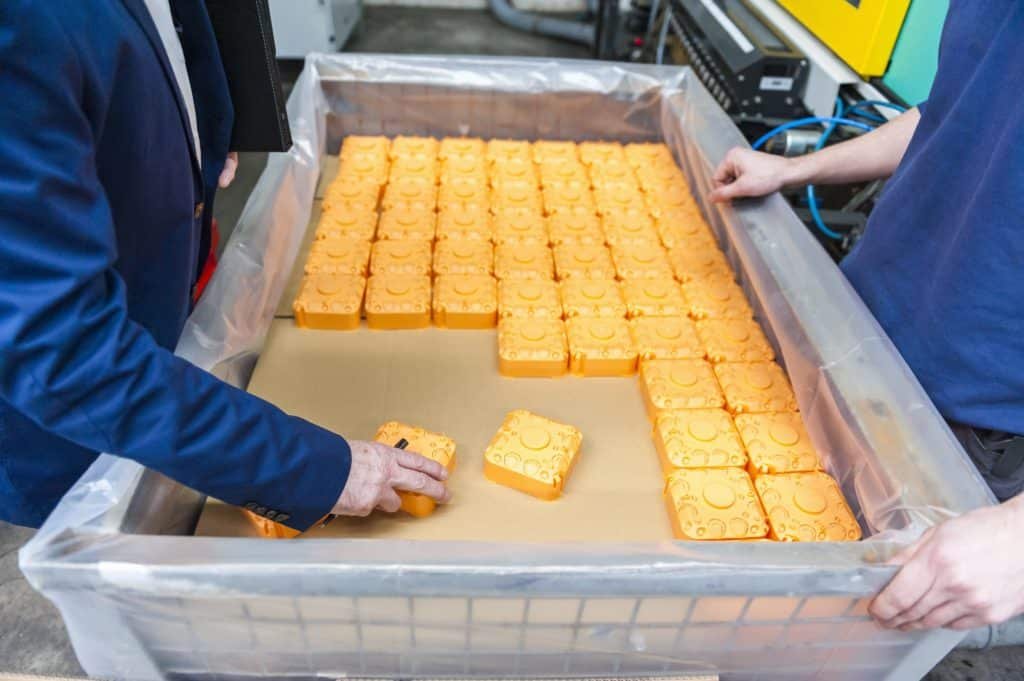
Quality Assurance:
Rigorous quality checks are conducted to ensure the molded products meet design specifications.
Defective items are identified and removed from the production line.

IV. Advantages of Injection Molding
High Precision and Complexity:
Injection Molding excels in producing intricate and complex components with high precision.
This makes it the method of choice for industries where detailed designs and tight tolerances are critical.
Versatility in Materials:
A wide range of materials, including thermoplastics, thermosetting polymers, and elastomers, can be used in the Injection Molding process.
Additives and reinforcements can be incorporated to enhance the material properties.

Conclusion:
As we delve into the intricacies of the Injection Molding process, it becomes evident that this method is more than just a manufacturing technique; it’s a precision-driven art form that shapes the world around us. From the meticulous injection of molten plastic to the careful cooling and post-processing steps, each phase contributes to the creation of products that define our daily lives. As industries continue to evolve, Injection Molding remains a linchpin, providing a reliable and efficient means of turning innovative designs into tangible reality.