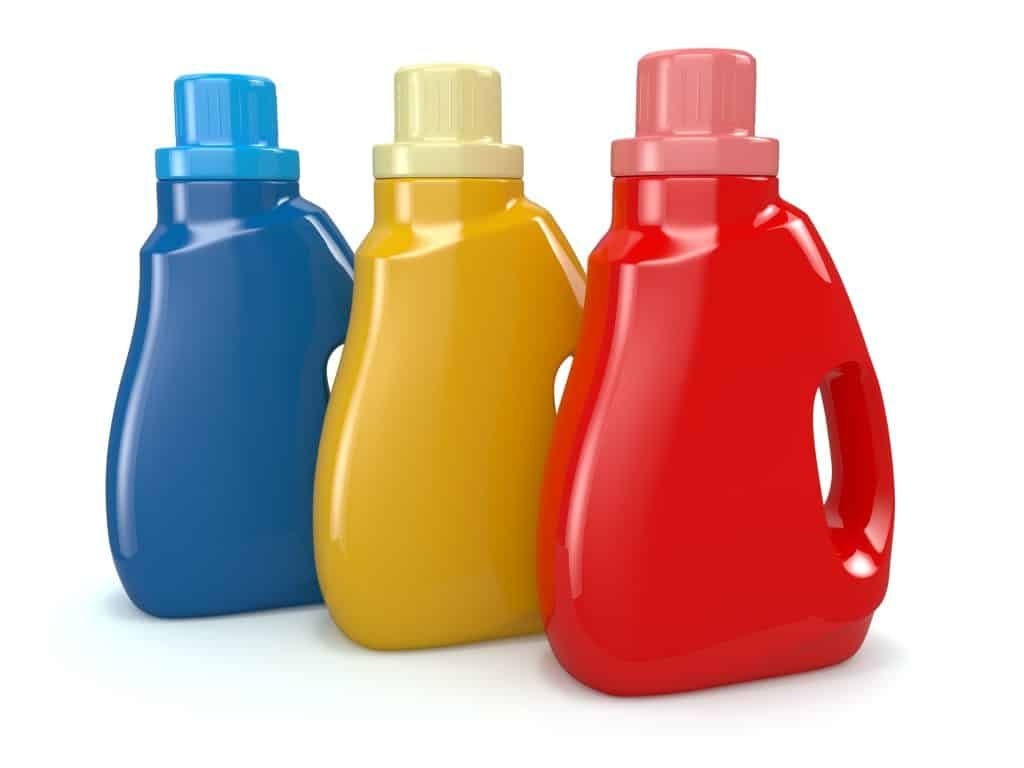
Plastic-colored products are affected by a variety of factors that can cause fading. The fading of plastic coloring products is related to the light, oxygen, heat, acid, and alkali resistance of the color powder, and the characteristics of the resin used.
The following is a detailed analysis of the factors that cause plastic coloring to fade:
1. Light fastness of colorant
The light fastness of the colorant directly affects product fading. It is important to use a colorant with high light fastness grade (6 or higher) for outdoor products exposed to strong light, while indoor products can use lower grades (4 or 5).
The carrier resin’s light resistance also influences color change and fading after ultraviolet irradiation. Adding UV absorbent and other light stabilizers to the masterbatch can improve the light resistance of colorants and colored plastic products.
2. Heat resistance
The thermal stability of heat-resistant pigments refers to their performance at processing temperatures in terms of weight loss, discoloration, and fading.
Inorganic pigments have good thermal stability due to their metal oxide composition, while organic compounds may undergo molecular structure changes at certain temperatures.
When selecting colorants for PP, PA, and PET products processed above 280℃, attention should be paid to pigment heat resistance and its time tolerance within this temperature range (usually 4-10 minutes).
3. Antioxidant properties
Some organic pigments degrade through oxidation processes leading to gradual fading under high temperature conditions or exposure to strong oxidants such as chromate in chromium yellow.
4. Acid and alkaline resistance
The chemical resistance (acid and alkali resistance) of coloring agents plays a role in product fading; for example, molybdenum chromium red is resistant to dilute acid but sensitive to alkali while cadmium yellow lacks acid resistance.
For addressing issues related to product fading from colored plastics comprehensive evaluation should be conducted on required pigments, dyes, surfactants, dispersants, carrier resins, and anti-aging additives according to processing conditions and use requirements of plastic products.