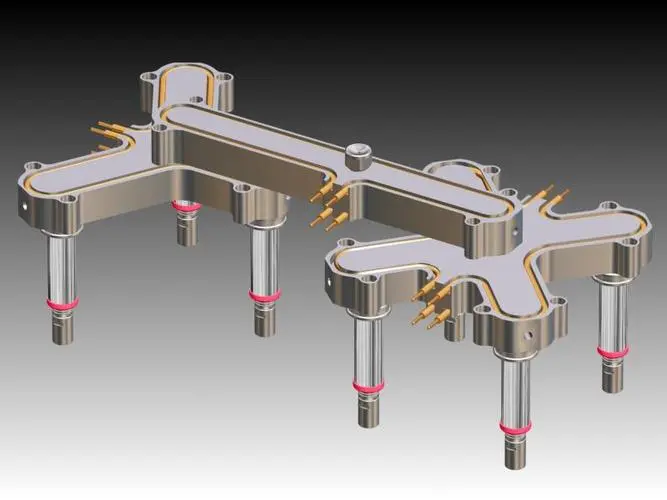
Injection molding is a prevalent manufacturing process used to produce a wide array of plastic products, ranging from simple household items to complex automotive components. A critical aspect of this process is the design and optimization of molds, particularly multi-cavity molds. Multi-cavity molds enable the simultaneous production of multiple parts in a single injection cycle, significantly enhancing productivity and reducing costs. However, optimizing multi-cavity molds for enhanced injection molding production requires careful consideration of various factors to ensure consistent quality and efficiency.
Understanding Multi-Cavity Molds
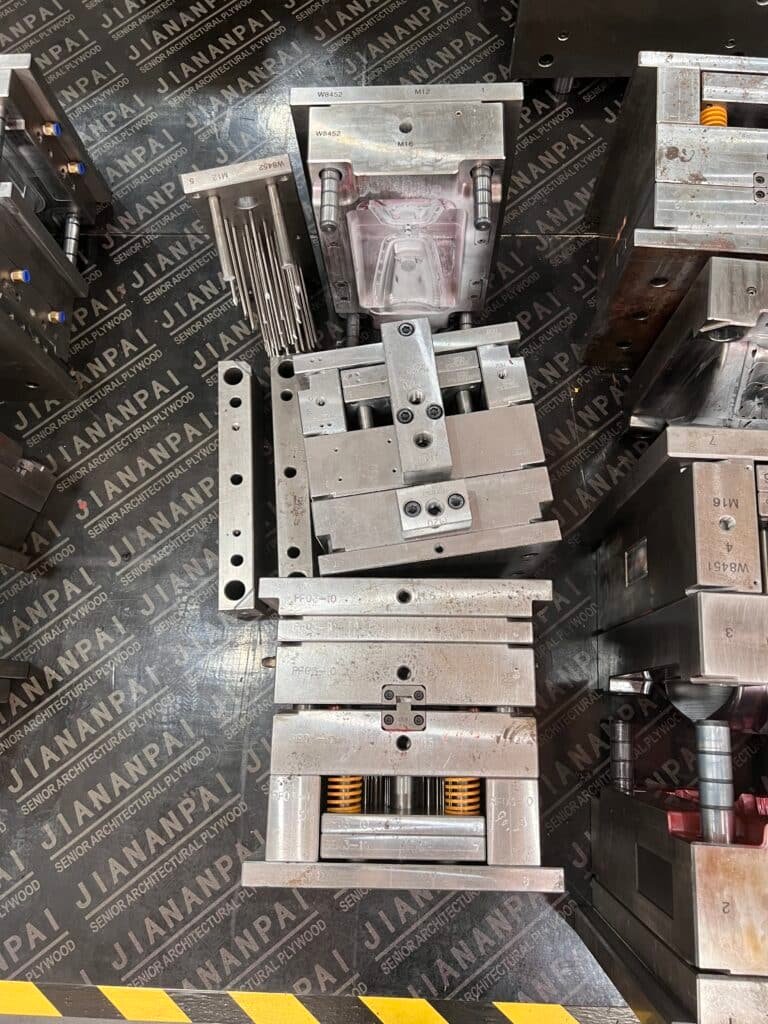
Multi-cavity molds have multiple cavities within a single mold base, each cavity producing one part per cycle. The key advantage of multi-cavity molds is their ability to produce multiple parts simultaneously, leading to higher output rates and reduced cycle times. This makes them particularly beneficial for high-volume production. However, the design and optimization of multi-cavity molds are more complex than single-cavity molds due to the need for uniform filling, consistent quality, and efficient cooling.
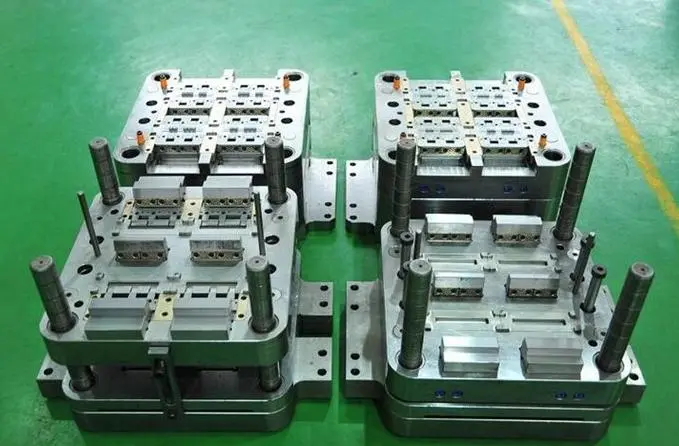

Key Considerations for Optimization
1. Mold Design and Layout
The design and layout of the mold are fundamental to achieving optimal performance. Factors to consider include:
- Cavity Arrangement: The arrangement of cavities should minimize the distance molten plastic must travel, ensuring uniform filling. Common layouts include balanced and symmetrical arrangements.
- Runner System: The runner system should be designed to balance the flow of molten plastic into each cavity. This involves the strategic placement of gates and runners to ensure equal pressure and temperature distribution.
- Cooling Channels: Efficient cooling is crucial to reduce cycle times and prevent defects. The design of cooling channels should provide uniform cooling across all cavities, minimizing thermal gradients and warpages.
2. Material Selection
The selection of the appropriate material for both the mold and the molded parts is critical. Mold materials should have high thermal conductivity, wear resistance, and strength to withstand the rigors of injection molding. For the molded parts, the material should have suitable flow properties, shrinkage rates, and mechanical properties to ensure high-quality production.

3. Process Parameters
Optimizing process parameters is essential for achieving consistent quality and efficiency. Key parameters to consider include:
- Injection Pressure and Speed: These should be adjusted to ensure uniform filling of all cavities without causing excessive stress or defects.
- Temperature Control: Maintaining consistent melt and mold temperatures is crucial for uniform flow and cooling. Advanced temperature control systems can help achieve this.
- Cycle Time: Reducing cycle time without compromising quality is a primary goal. This involves optimizing injection, cooling, and ejection phases.
4. Simulation and Analysis
Using computer-aided engineering (CAE) tools for mold flow simulation can significantly enhance the optimization process. Simulation allows for the prediction of flow behavior, cooling efficiency, and potential defects, enabling designers to make informed decisions and adjustments before actual production.
Strategies for Enhanced Production
1. Balanced Filling
Ensuring balanced filling of all cavities is essential for consistent quality. This can be achieved through:
- Flow Analysis: Conduct flow analysis to identify potential imbalances and adjust the runner and gate design accordingly.
- Valve Gates: Utilizing valve gates can provide precise control over the filling process, ensuring each cavity fills uniformly.
2. Efficient Cooling
Effective cooling is vital for reducing cycle times and preventing defects. Strategies include:
- Conformal Cooling Channels: These channels conform to the shape of the part, providing more efficient and uniform cooling compared to traditional straight-line channels.
- Advanced Cooling Technologies: Technologies such as baffles, bubblers, and heat pipes can enhance cooling efficiency.
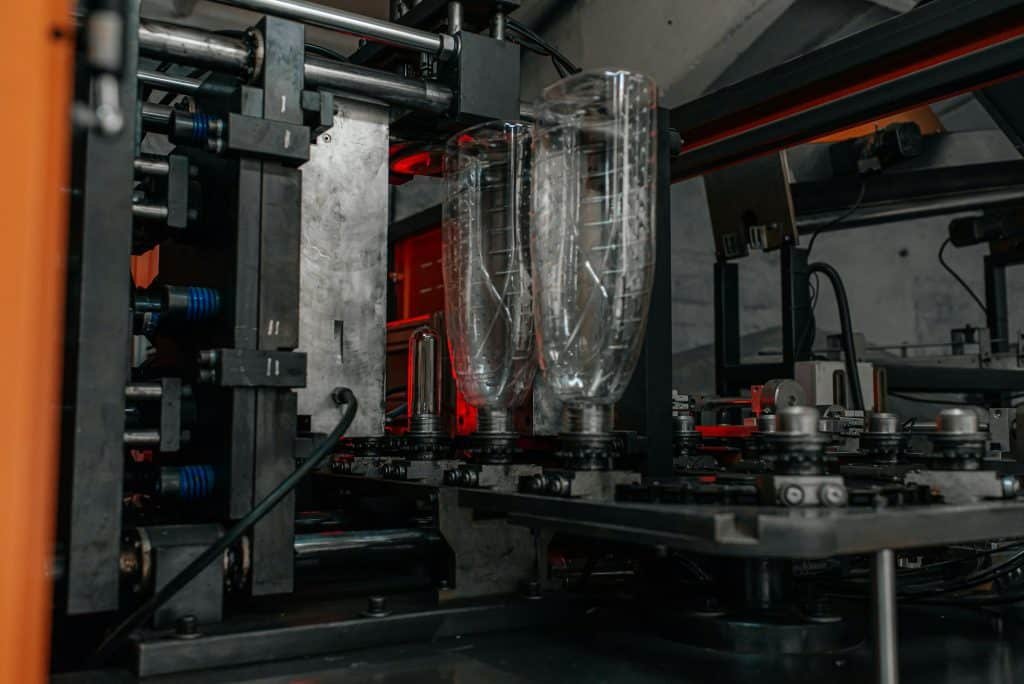

3. Quality Control
Maintaining high quality across all cavities requires robust quality control measures, including:
- In-Mold Sensors: Using sensors to monitor temperature, pressure, and flow within the mold can provide real-time data for process adjustments.
- Regular Maintenance: Performing regular maintenance on the mold and machinery to prevent wear and tear that can lead to defects.
Case Studies and Applications
1. Automotive Industry
In the automotive industry, multi-cavity molds are used to produce components like dashboard panels, door handles, and engine covers. Optimizing these molds involves ensuring uniform quality across all cavities to meet stringent safety and performance standards. Techniques such as flow simulation, valve gates, and advanced cooling systems are commonly employed.

2. Consumer Goods
For high-volume consumer goods like bottle caps, optimizing multi-cavity molds is crucial for meeting demand and maintaining cost-effectiveness. Efficient runner systems, rapid cycle times, and robust quality control measures are essential in this sector.

Future Trends
The future of multi-cavity mold optimization lies in advancements in technology and materials. Emerging trends include:
- 3D Printing of Molds: Additive manufacturing allows for the creation of complex mold geometries and conformal cooling channels, enhancing performance and reducing lead times.
- Smart Manufacturing: The integration of IoT and AI in injection molding can provide real-time monitoring and predictive maintenance, further optimizing production efficiency.
Optimizing multi-cavity molds for enhanced injection molding production is a multifaceted process that involves careful consideration of mold design, material selection, process parameters, and advanced simulation techniques. By implementing strategies such as balanced filling, efficient cooling, and robust quality control, manufacturers can achieve higher productivity, consistent quality, and reduced costs. As technology continues to advance, the future holds promising opportunities for further optimization and innovation in the field of injection molding.