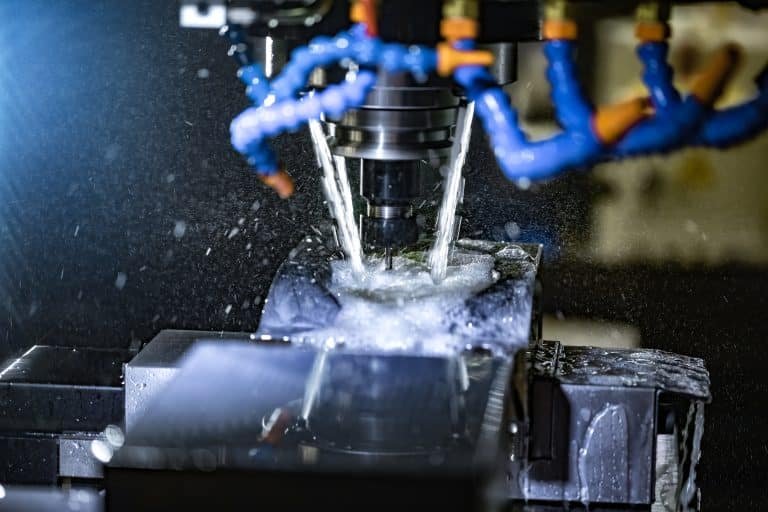
Injection molding is one of the most effective and common manufacturing processes in the automotive, electronics, medical devices, and consumer goods industries. Creating injection molds is a vital process whether you are a novice or an experienced professional, you need to know how to create injection molds. BFY Mold will lead you through the most important considerations, stages, advantages, and how injection molds are created at the industrial level and in the home.
What are the Factors that Create Injection Molds?
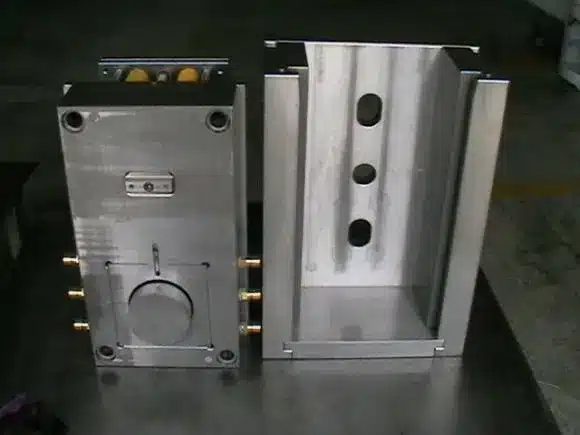

For making good injection molds, some factors should be considered to maintain the process and performance of custom injection molds. The following factors influence the process:
1. Material Selection
The performance allotted to a mold is mainly dependent on the material used for the manufacturing of the mold. Common types of materials include:
Steel: Strong and durable, yet costly and labor-intensive to machine.
Aluminum: Light, easier to machine but less durable than steel, hard but suitable for short production runs.
Copper Alloys: Provide good thermal conductivity but may be expensive.

2. Design Considerations
Effective mold design ensures product quality and minimizes defects. Key design elements include:
Parting line: The line where the two halves of the mold meet, which affects the part’s appearance and functionality.
Gate design: Type and position of the gate from which molten metal flows into the cavity.
Ejection system: How the finished part will be removed without being damaged.
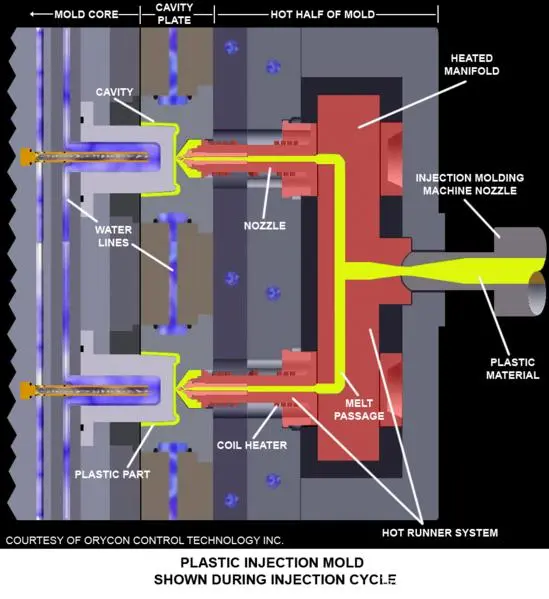
3. Mold Complexity
The simplicity of the mold affects the time and cost of production directly. Molds with more complex features require sophisticated tools and processes, resulting in increased cost and lead time.
4. Mold Cooling
Within the mold, cooling systems help keep everything homogeneous as far as part quality. Overheating may cause defects such as warping, so adequate cooling channels are critical.
The Steps in the Injection Mold-Making Process
The process of making an injection mold is complex and consists of different stages, from the final design to the final testing. Here is a breakdown of the major steps:
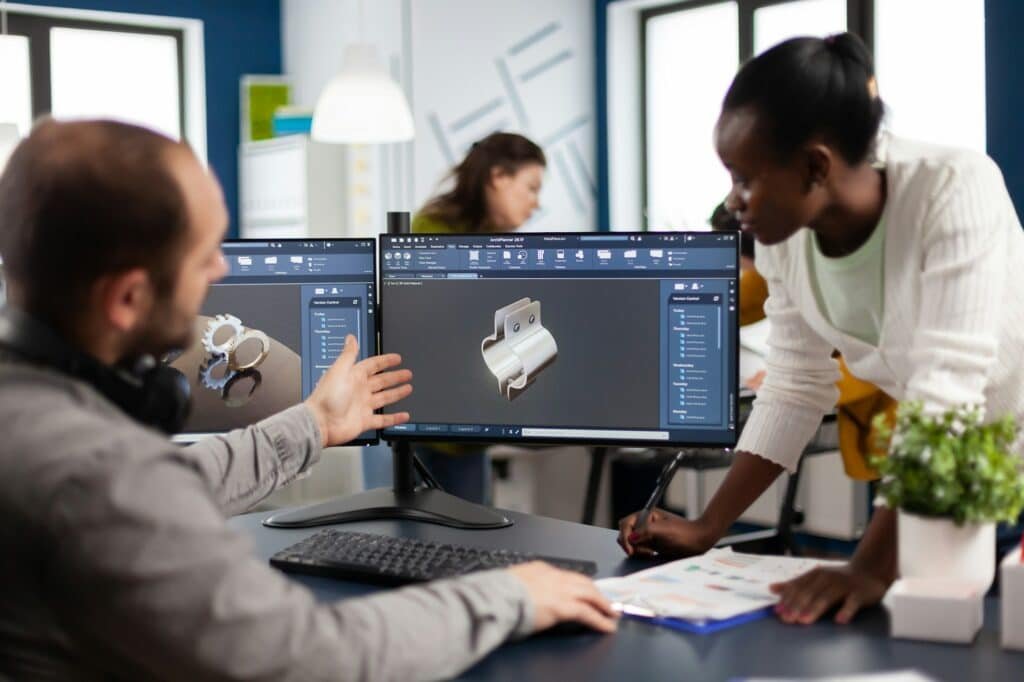
Stage 1: Injection Mold Design and Prototyping
Firstly, this is where you make the fully defined design of the part and the molds. This phase often includes:
3D modeling: Visualizing the part and the mold with CAD software.
Prototype testing: Quick prototyping to validate the functionality of the design before rolling into production.


Stage 2: Injection Mold Construction
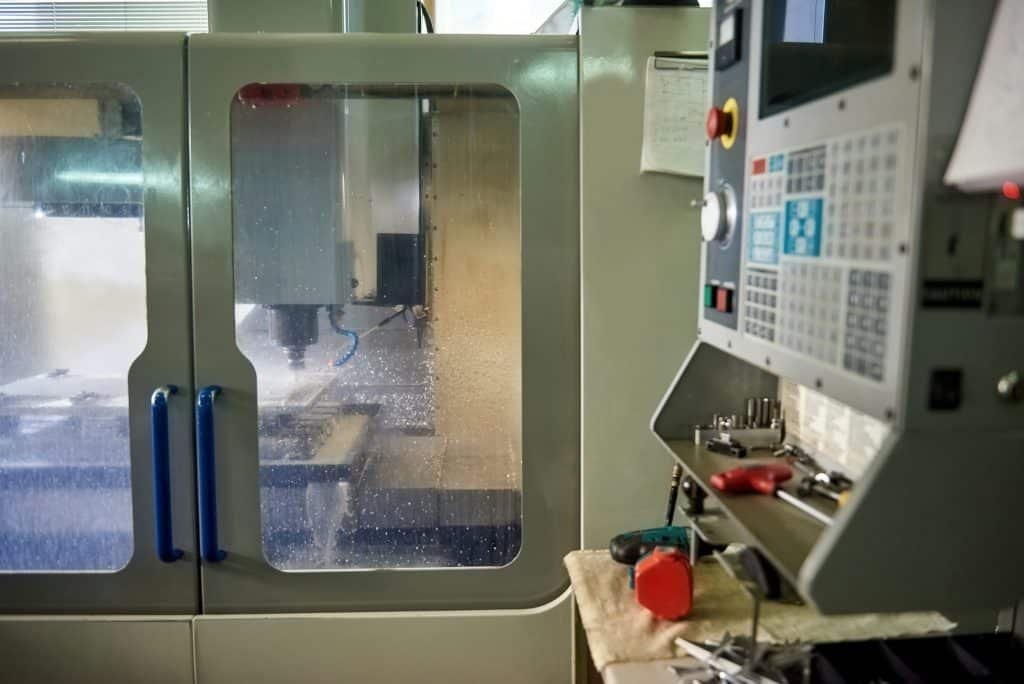
After the design is approved, the mold can be built. This phase involves:
CNC machining: Using precise machinery to carve out the features of the mold.
Electro-discharge machining (EDM): Useful for adding fine details that are hard to machine directly.
Assembly: Putting everything right from the cooling systems to the ejector pins and cavities in this mold.

Stage 3: Adjusting based on mold test results
The mold is then used to cast several prototypes and tested until it meets specs before full-scale production can be launched. The testing phase includes:
Test parts: Making pieces to check that things are operating as they should
Corrections: Adjustments to the mold after trial data; such as the position of the gate, cooling performance, etc.
Stage 4: Production
After testing and adjustments to the mold, full-scale production can begin. This stage involves:
Injection molding: The actual injection of molten plastic or metal into the cavity of the mold.
Quality assurance: Continuous verification process to ensure each component is consistent and of the utmost quality.
In-House & High Volume Injection Molds Advantages
a: Cost Efficiency
In-house mold making can help save on outsourcing costs such as shipping and design fees and markup costs. Economies of scale bring down further the price per unit with mass manufacture.
b: Customization
On the other hand, creating molds in-house gives manufacturers more control over the design process. This guarantees that the molds conform to specific requirements, producing better-quality products with fewer imperfections.
c: Speed
Making molds in-house usually results in a quicker turnaround. This technological advancement enables companies to iterate quickly through design changes while tackling problems, thus shortening the total time it takes to go into production.
d: Protection of Intellectual Property
In-house mold manufacturing allows companies to maintain better control of the intellectual property involved in the mold-making process and helps prevent leaks of work-intensive design information.
How Injection Molding Works in an Industry
So the process for making injection molds is more complex and relies on multiple advanced technologies in industrial settings. Here’s a glimpse of how molds are produced in industrial settings:
High-Precision Equipment
In industrial injection molding, we usually use advanced machines, including CNC machines, EDM machines, and high-performance injection molding machines. These machines provide a high level of precision, allowing parts to be produced with tight tolerances.
Automated Systems
Automation plays an important role in industrial mold-making. Automated systems assist with several processes, including mold assembly, part ejection, and quality inspection; decreasing human error and increasing speed.
Skilled Workforce
This process requires well-experienced engineers, mold makers, and technicians to create industrial molds. They know that molds must be designed and manufactured to high standards for both performance and quality.
Advanced Testing
From Healthcare to Automotive, Industries Depend on Testing and Quality Control This typically entails advanced testing techniques, such as digital simulations, to tweak the mold ahead of widespread production.
DIY Injection Molding: A Fast Turnaround for Low Volumes
Creating injection molds doesn’t always need industrial-scale equipment, especially for hobbyists or small businesses. Injection molding is a relatively simple process and can even be done in your garage for small-batch production or prototyping. The process involves:
1. Injecting Machines of a Small Scale
There are even small tabletop injection molding machines that can build your molds. These are great for small parts or prototypes and much more affordable than large industrial machines.
2. Simple Molds
The design of both is typically different: industrial molds are usually complex, while the DIY mold is much simpler and easier to move. Instead, the molds can be constructed from more easily manipulatable materials such as silicon or aluminum on a smaller scale.
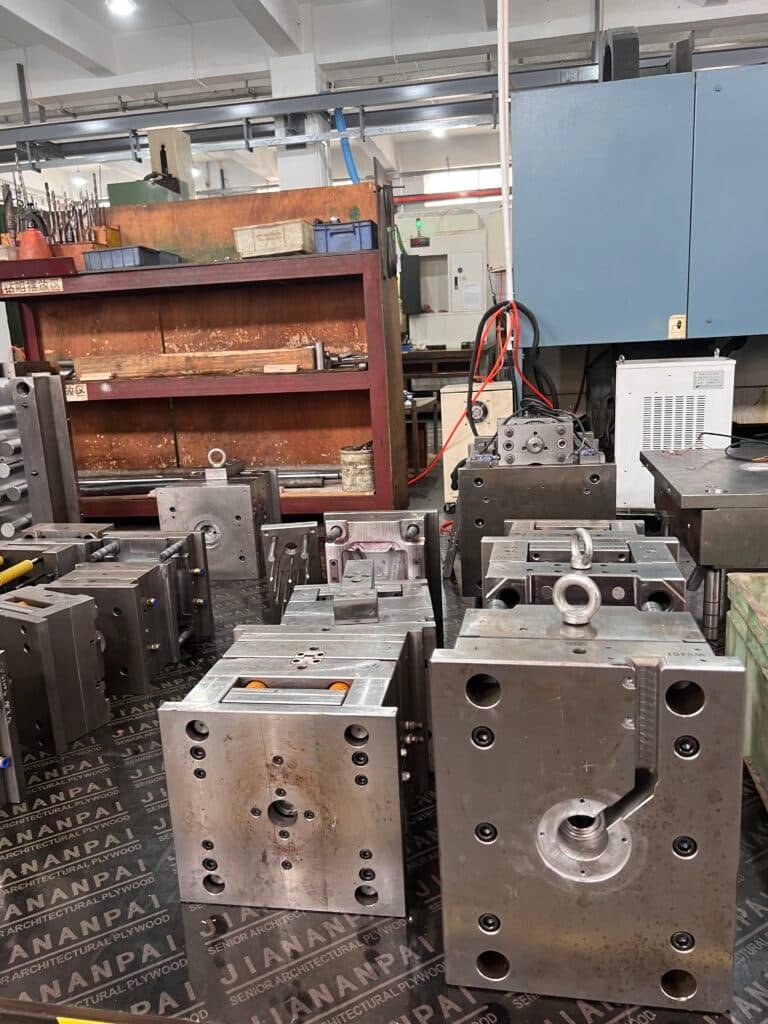

3. Manual Injection
In DIY injection molding, molten plastic is sometimes injected by hand into the mold. This involves less sophisticated gear and enables rapid testing of various materials.
4. Limited Production Runs
DIY molding usually is only done in small production runs or prototypes due to the nature of the equipment and molds used to create them. It can be an industrial-scale test to do so before moving up to full-blown production.
Reasons to Consider BFY Mold for Your Injection Molding Needs

Our services include:
- Injection Molds Making: Molds complex parts with precision.
- Injection Molding: Advanced molding services to produce high-quality plastic parts.
- Mass Production & On-Demand Production: Scalable solutions to produce what you need.
- Molding capabilities are supplemented by CNC Machining & Mirror Spark: High Precision Machining Services
We own a complete plant, which helps us to offer speedy, economical, and quality solutions for your injection molding applications. We have the experience to handle every job with diligence and care.









