In the vast realm of modern manufacturing, the process of plastic injection molding stands as a linchpin, shaping the production landscape of a myriad of industries. As manufacturers strive for efficiency, precision, and cost-effectiveness, understanding the intricate dynamics that govern the cost of plastic injection molding becomes paramount. This introductory essay delves into the multifaceted world of plastic injection molding costs, unraveling the primary factors that influence them and exploring strategic avenues for cost reduction.
Before delving into the intricacies of cost, it is crucial to grasp the fundamentals of plastic injection molding. This manufacturing process involves injecting molten plastic material into a mold cavity, allowing it to cool and solidify to form a specific shape. Known for its versatility, scalability, and ability to produce complex designs with high precision, plastic injection molding has become the go-to method for the mass production of a diverse range of products.
Factors Influencing the Injection Molding Cost:
The cost of plastic injection molding is an amalgamation of various factors, each playing a pivotal role in determining the overall expense associated with the process. Understanding these factors is essential for manufacturers seeking to optimize their production costs and remain competitive in the global market. The key elements influencing the cost of plastic injection molding include:

1. Raw Material Costs:
The choice of plastic resin significantly impacts the overall cost. Different resins come with varying price points, and considerations such as material strength, durability, and intended use must be factored into the decision-making process. Fluctuations in raw material prices, influenced by global market trends and geopolitical factors, can also introduce an element of volatility into the cost equation.
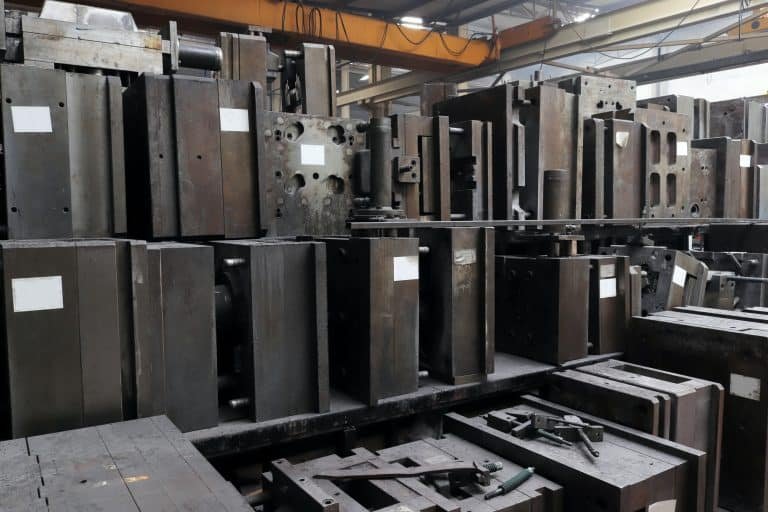
2. Mold Tooling Expenses:
The creation and maintenance of molds constitute a substantial portion of the upfront costs of plastic injection molding. The complexity of the mold design, the type of material used for the mold, and the anticipated production volume all contribute to the overall tooling expenses. Investments in high-quality molds often yield long-term benefits by reducing defects and improving production efficiency.

3. Machine and Labor Costs:
The efficiency of the injection molding machines, their cycle times, and the level of automation in the production process directly impact costs. Skilled labor is required for machine operation, quality control, and maintenance. Labor costs can vary significantly based on the geographical location of the manufacturing facility, with regions having lower wage rates often enjoying a cost advantage.
4. Energy Expenditures:
Injection molding is an energy-intensive process, and the cost of energy, including electricity and other utilities, contributes to the overall production expenses. Implementing energy-efficient technologies, optimizing machine settings, and adopting sustainable practices can mitigate the impact of energy costs on the overall budget.
5. Regulatory Compliance:
Different regions and industries may have distinct regulatory requirements and standards that manufacturers must adhere to. Compliance with environmental regulations, safety standards, and quality certifications can influence the cost of plastic injection molding. Failure to meet these standards may result in fines, rework costs, and damage to the reputation of the manufacturing entity.
Reducing the Cost of Plastic Injection Molding:
In the quest for cost optimization, manufacturers can adopt strategic measures to enhance efficiency and mitigate expenses. Here are key strategies to consider:
1. Material Selection and Optimization:
Careful consideration of the specific requirements of the end product allows manufacturers to choose materials that strike a balance between performance and cost. Utilizing recycled or bio-based plastics can also align with sustainability goals while potentially reducing material costs.
2. Efficient Mold Design and Maintenance:
Investing in well-designed, durable molds can yield long-term cost savings. Regular maintenance and preventive measures can extend the lifespan of molds, reducing the frequency of replacements and minimizing downtime.

3. Automation and Technology Integration:
Embracing automation and advanced technologies in injection molding processes can enhance efficiency, reduce cycle times, and minimize labor costs. Robotics and sensor technologies can be employed to automate tasks, ensuring precision and consistency in production.
4. Energy Efficiency Practices:
Implementing energy-efficient machinery and optimizing production processes can result in substantial savings on energy expenditures. Manufacturers can conduct energy audits to identify areas for improvement and invest in technologies that minimize energy consumption.
5. Lean Manufacturing Principles:
Adopting lean manufacturing principles helps eliminate waste, streamline processes, and enhance overall efficiency. Just-in-time production, optimized inventory management, and continuous improvement practices contribute to cost reduction.

6. Supplier Collaboration:
Building strong partnerships with suppliers can lead to cost advantages. Negotiating favorable terms for raw materials, exploring bulk purchasing options, and collaborating on process optimization initiatives can create a mutually beneficial relationship.
7. Geographical Considerations:
Evaluating the geographical location of manufacturing facilities can impact labor costs, regulatory compliance, and logistics expenses. While lower labor costs may be attractive in certain regions, other factors, such as shipping costs and trade regulations, should also be taken into account.
Conclusion:
As manufacturers navigate the complex terrain of plastic injection molding, understanding the nuanced factors influencing costs is pivotal for strategic decision-making. From raw material selection to efficient mold design, embracing technological advancements, and optimizing energy consumption, the quest for cost reduction requires a multifaceted approach. In this dynamic landscape, where economic considerations and technological innovations intersect, manufacturers can uncover opportunities to not only minimize costs but also enhance the overall sustainability and competitiveness of their plastic injection molding processes.









