Injection molding is a highly efficient manufacturing process used to produce a wide range of plastic parts, from everyday items like toothbrushes and bottle caps to complex components for automotive and medical applications. The process involves injecting molten plastic into a mold cavity, where it cools and solidifies into the desired shape. While injection molding offers significant advantages in terms of scalability, precision, and production speed, cost management remains a critical aspect for manufacturers looking to stay competitive.
Understanding Injection Molding
Before delving into cost-saving strategies, it’s essential to grasp the basic components and steps of the injection molding process:
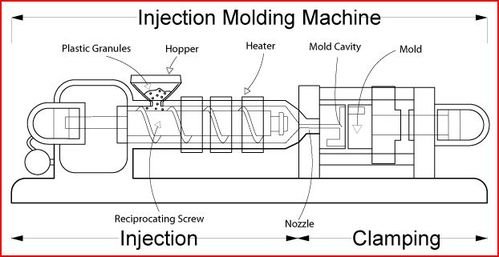
Injection Molding Process
- Material Preparation: Thermoplastic pellets are fed into the injection molding machine’s hopper, where they are heated until they melt.
- Injection: The molten plastic is injected into the mold cavity under high pressure using a screw or ram injector.
- Cooling: The mold is cooled, allowing the plastic to solidify into the final part shape.
- Ejection: Once the part has solidified, it is ejected from the mold for further processing or packaging.
Each step of this process offers opportunities for cost optimization. Below are some simple ways to save injection molding costs, along with relevant parameter cases.
How to Save Injection Molding Costs?
Material Selection and Optimization
Choosing the right material is crucial for balancing performance and cost. High-quality materials often come with a higher price tag, but opting for cheaper alternatives without compromising the product’s integrity can lead to significant savings.
A company manufacturing outdoor plastic furniture switched from using polycarbonate (PC) to a high-impact polypropylene (PP) blend. This change reduced material costs by 30% while maintaining the required durability and UV resistance.
Cycle Time Reduction
Minimizing the cycle time – the duration required to complete one production cycle – directly impacts productivity and cost. Strategies to reduce cycle time include optimizing cooling time, improving mold design, and using advanced machinery.
By implementing conformal cooling channels in their molds, a manufacturer reduced the cooling time from 20 seconds to 12 seconds per cycle. This resulted in a 40% increase in production rate, significantly lowering labor and overhead costs.
Minimizing Material Waste
Material waste can occur in various forms, such as sprues, runners, and defective parts. Reducing waste not only saves on raw material costs but also decreases disposal expenses.

PET injection molding cost
Energy Efficiency
Energy consumption is a significant cost factor in injection molding. Utilizing energy-efficient machinery and optimizing machine settings can lead to substantial savings.
Improving Mold Design
Investing in high-quality mold design can reduce long-term costs by minimizing defects, reducing cycle times, and enhancing overall production efficiency.
A medical device manufacturer implemented a multi-cavity mold design, allowing them to produce eight parts per cycle instead of four. This upgrade doubled their output and reduced per-part costs by 20%.

Optimizing Maintenance Practices
Regular maintenance of injection molding machines and molds prevents unexpected downtime and costly repairs. Predictive maintenance strategies can further enhance efficiency.
Automation and Labor Reduction
Automation of repetitive tasks can significantly reduce labor costs and increase production efficiency. Incorporating robots for part handling, quality inspection, and packaging can streamline operations.
Some automotive parts manufacturers integrated robotic arms into their injection molding process for part removal and assembly. This automation reduced labor costs by 30% and increased production throughput by 25%.

Conclusion
Injection molding is a versatile and efficient manufacturing process, but controlling injection molding costs is essential for maintaining competitiveness in the market. By focusing on material optimization, cycle time reduction, waste minimization, energy efficiency, and other cost-saving strategies, manufacturers can significantly reduce expenses while maintaining high-quality production standards. Real-world parameter cases illustrate how these strategies can be successfully implemented, providing valuable insights for companies looking to enhance their injection molding operations. Adopting a holistic approach to cost management ensures long-term sustainability and profitability in the ever-evolving manufacturing landscape.









