In over-molding, careful positioning of rigid components is necessary, ensuring scalability and incorporating draft holes to prevent part distortion.
Two-shot molding, increasingly popular in the market, enhances product aesthetics without the need for painting, yet it’s costly and demands advanced skills.
Whether two-shot molding or over-molding, both employ two types of plastic composite injection: first, rigid parts, then soft parts. Though similar, they are distinct processes. Below, BFY mold engineers delineate the disparities.
Differences Between Two-Shot Molding and Overmolding
A. Two-Shot Molding
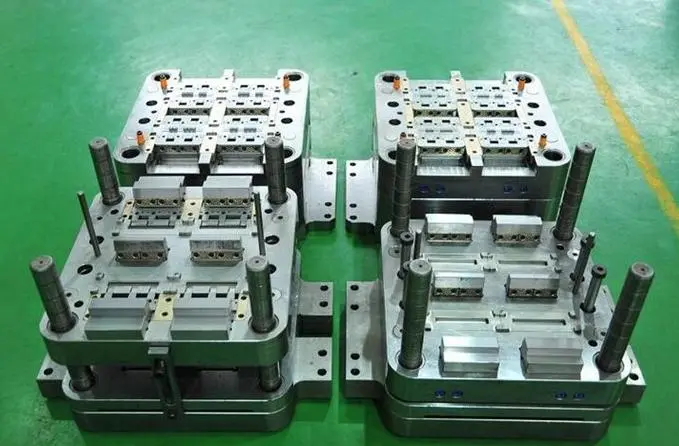

Two plastic materials are injected into the same machine in two steps, with a single-mold product output. Often termed as dual-material injection, typically completed with one mold set and requires a dedicated two-shot injection machine.
Two-shot molds merge two resin types and colors into a single product, reducing assembly and post-processing. This approach saves costs on bonding and printing, elevates visual appeal, and enhances product quality and value. Additionally, it provides functionality like anti-slip properties and improved ergonomic feel.

Two-shot injection offers high product quality, manageable deformation, shorter cycle times, and higher yields compared to over-molding, with 7% lower material wastage and 20%-30% lower manufacturing costs.
B. Overmolding (Secondary Molding)
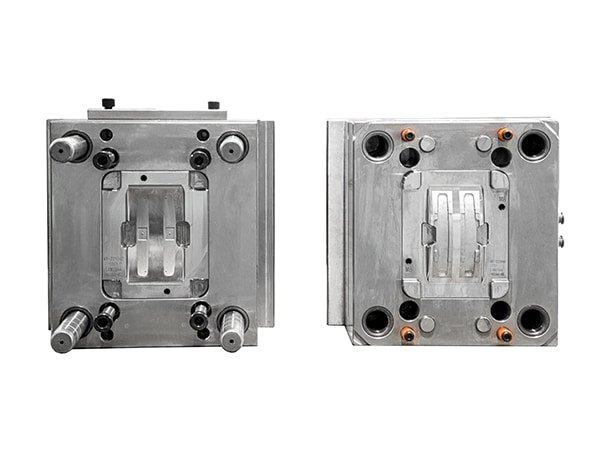

Two plastic materials may not be injected on the same machine, undergoing two-step molding. After ejection from one mold set, products enter another for secondary molding. Hence, this method typically requires two mold sets and no specific two-shot injection machine. The mold structure is similar to that of single-color injection molds, primarily relying on adjusting injection parameters for material fusion points.
Overmolding mainly encapsulates a soft material over a hard one, with common materials like TPU, TPR for soft parts, ABS, PC, and PP for rigid components.
Additional Points of Contrast:
1. Cavity shapes differ for each molding method, forming distinct products, while core shapes remain identical.
2. Alignment of the front and rear molds must be ensured after rotating 180 degrees. This check is crucial during design.
3. Attention is required for the location of pinholes, with a small distance of 210mm. Larger molds may need additional pin holes, with elongated pins designed within the mold, due to insufficient length in the injection machine. Two locating rings should be placed on the rear mold base.
4. The total thickness of the front mold panel and A plate should not be less than 170mm. Carefully examine other reference data for this injection machine model, including large and small mold thicknesses and pinhole distances.
5. For three-plate molds, design the gates for automatic ejection where possible, especially ensuring the feasibility of ejection for soft material gates.
6. The depth of the front-side sprue should not exceed 65mm. The distance from the top of the upper sprue to the center of the mold embryo should be at least 150mm.
7. To avoid cavity damage during the second injection, consider designing some void spaces in the first-formed product position. However, ensure the strength of each sealing point, considering potential deformation under high injection pressure during the second molding.
8. Allow the first-formed product dimensions to be slightly larger during injection to ensure tighter compression with the other cavity in the second molding, achieving sealing.
9. Assess if the flow of plastic during the second injection may affect the first-formed product, potentially causing deformation. If so, seek improvements.
10. Before closing the A and B plates, ensure the front mold slider or lifter does not damage the product during repositioning. If so, find a solution to ensure the A and B plates close first, followed by the slider or lifter resetting.
11. Optimize and balance the waterways for both cavity and core to ensure uniform flow.
12. In 99% of cases, inject the rigid part first, followed by the soft part, as the latter is more prone to deformation.









