In the world of manufacturing, vacuum casting, and injection molding are two widely used techniques for creating parts and products. Each method has its unique strengths, applications, and nuances. This article explores these processes in detail, offering insights into their lead times, production volumes, costs, tolerances, and more to help you make an informed decision.
Vacuum Casting Guide
What is Vacuum Casting?
Vacuum casting, also known as urethane casting, is a manufacturing process primarily used for producing prototypes and small batches of parts. The process begins with creating a master model, typically through 3D printing or CNC machining. This model is then encased in silicone to form a mold. The mold is filled with liquid resin under vacuum conditions to remove air bubbles and ensure a high-quality finish.

What is the Lead Time for Vacuum Casting Production?
The lead time for vacuum casting is relatively short. Creating silicone molds and casting parts can be completed within a few days to a couple of weeks, depending on the complexity and number of parts. This quick turnaround makes vacuum casting ideal for rapid prototyping and short production runs.
How is the Production Volume of Vacuum Casting?
Vacuum casting is best suited for low-volume production. It is typically used for creating prototypes and small batches, usually up to 100 parts. This method is ideal for projects requiring high-quality, detailed parts without the need for large quantities.
What Are the Tools and Parts Costs for Vacuum Casting?
The initial costs for vacuum casting are relatively low, mainly due to the inexpensive silicone molds. However, the price per part can be higher compared to other methods because each mold has a limited lifespan and can produce only a finite number of parts before needing replacement.

What is the Tolerance of Vacuum Casting?
Vacuum casting offers good dimensional tolerances, often within ±0.1mm. The exact tolerance depends on the complexity of the part and the materials used. This precision makes vacuum casting suitable for producing detailed and intricate components.
Injection Molding Guide
What is Injection Molding?
Injection molding is a manufacturing process used for producing large quantities of parts. The process involves melting plastic material and injecting it into a metal mold under high pressure. Once the material cools and solidifies, the mold opens, and the part is ejected.
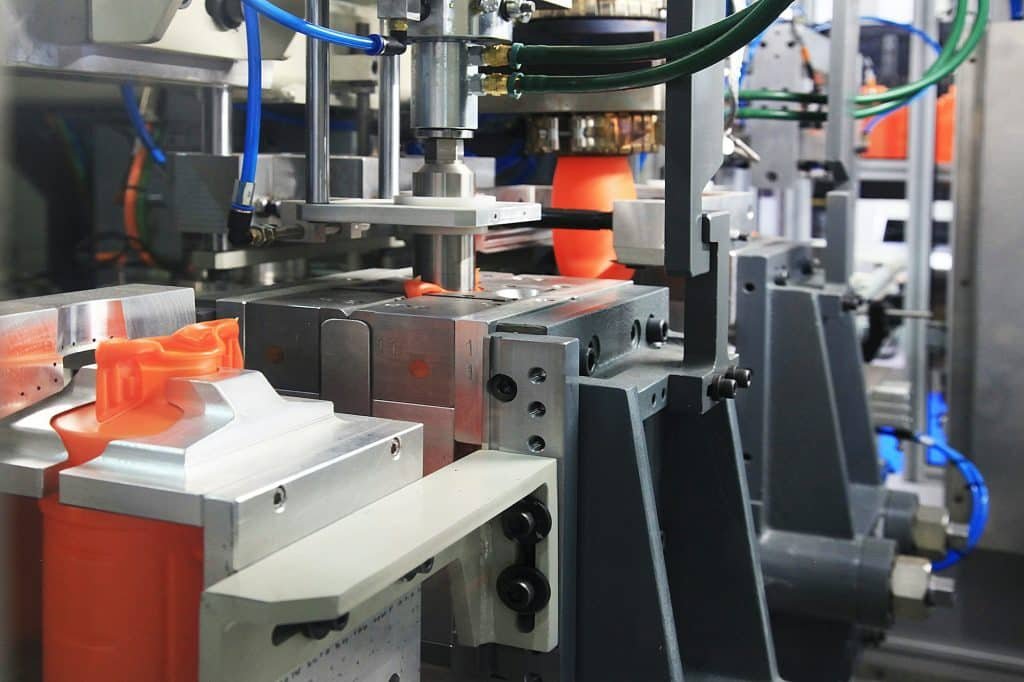

What is the Lead Time for Injection Molding Production?
The lead time for injection molding is generally longer than vacuum casting due to the time required to design and manufacture the metal molds. This process can take several weeks to a few months. However, once the mold is ready, the production of parts is rapid and efficient.
How is the Production Volume of Injection Molding?
Injection molding is ideal for high-volume production. It can efficiently produce large quantities of parts, making it suitable for mass production runs. This method is commonly used in industries like automotive, electronics, and consumer goods.
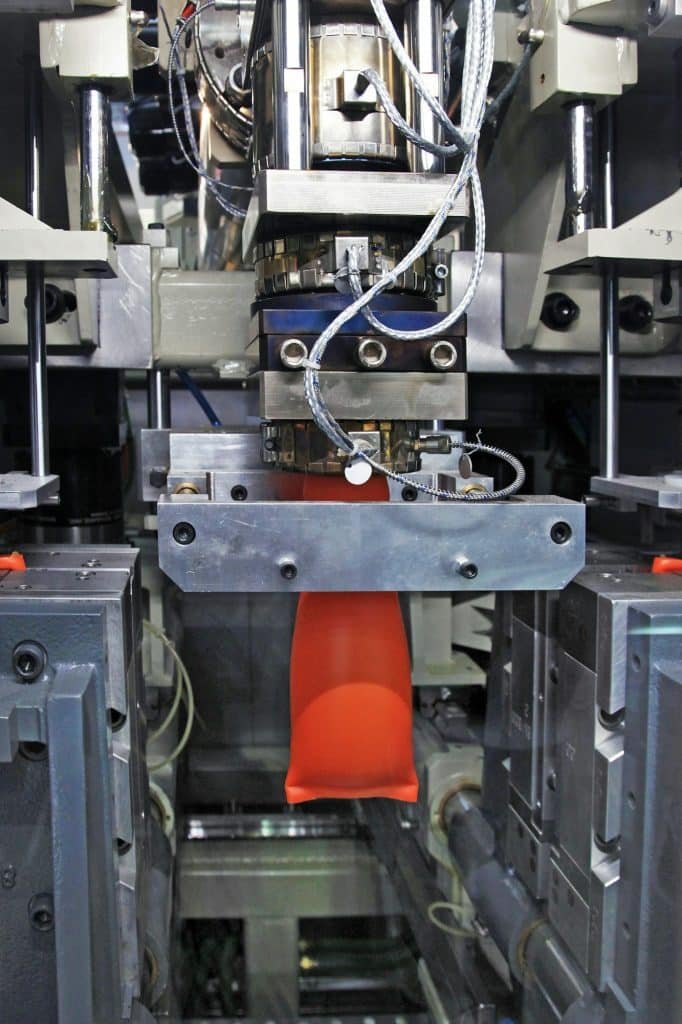
What Are the Tools and Parts Costs for Injection Molding?
The initial cost for injection molding is high due to the expense involved in creating the metal molds. However, the cost per part decreases significantly with higher production volumes, making it a cost-effective solution for large-scale manufacturing.
What is the Tolerance of Injection Molding?
Injection molding offers excellent dimensional tolerances, often within ±0.01mm. This high level of precision makes it suitable for producing complex and intricate parts with stringent requirements.
Making the Right Choice
How to Choose the Right Manufacturing Process?
Choosing between vacuum casting and injection molding depends on several factors, including production volume, lead time, material requirements, and budget. Here’s a comparison to help guide your decision:
- Production Volume: For low-volume runs and prototypes, vacuum casting is more cost-effective. For high-volume production, injection molding is the better choice.
- Lead Time: If quick turnaround is crucial, vacuum casting is preferable due to its shorter lead times. Injection molding requires a longer setup time but offers rapid production once the mold is ready.
- Cost: Vacuum casting has lower initial costs but higher per-part costs for larger volumes. Injection molding has high initial costs but becomes more economical with higher volumes.
- Material and Precision: Both methods offer a range of materials, but injection molding provides better precision and repeatability for complex parts.
Key Differences Between Vacuum Casting and Injection Molding
Vacuum Casting:
- Best for small batches and prototypes.
- Quick lead times.
- Lower initial costs but higher per-part costs for larger volumes.
- Good detail and surface finish.
- Tolerances around ±0.1mm.
Injection Molding:
- Ideal for high-volume production.
- Longer lead times for mold creation but faster production rates.
- High initial costs but lower per-part costs for large runs.
- Excellent precision and repeatability.
- Tolerances around ±0.01mm.
Summary
In conclusion, both vacuum casting and injection molding offer unique strengths and are suitable for different manufacturing needs. Understanding the specific requirements of your project will help you choose the most appropriate process, ensuring cost-effectiveness, efficiency, and high-quality results.









