Introduction
In low-volume manufacturing (1–10,000 units), choosing the right mold material is critical to balancing cost, speed, and quality. While steel molds dominate high-volume industries, aluminum molds are increasingly favored for prototypes and small batches.
BFY Mold’s analysis, backed by 50+ client projects, reveals how aluminum molds deliver 30–50% cost savings, 60% faster turnaround, and unmatched adaptability for iterative designs. Here’s why they outperform steel in low-volume scenarios.

1. Aluminum vs. Steel: Key Property Comparison
| Factor | Aluminum Molds | Steel Molds |
| Tooling Cost | 8,000–15,000 | 25,000–60,000 |
| Machining Time | 2–3 weeks | 6–12 weeks |
| Thermal Conductivity | 130–150 W/m·K | 15–50 W/m·K |
| Tool Life | 10,000–100,000 shots | 500,000–1M+ shots |
| Modification Cost | Low (soft material) | High (hardened steel) |

2. 4 Reasons Aluminum Dominates Low-Volume Production
① Faster Time-to-Market
- Rapid Machining: Aluminum’s softness allows CNC milling at 3x steel’s speed.
- Case: A consumer electronics customer used aluminum molds to complete a smart home shell trial production within 18 days, reducing the delivery cycle by 70% compared to steel molds.
② Lower Upfront Costs
- Material Savings: 7075-T6 aluminum costs ~30/kg. P20steel’s 30/kg. P20 steel’s 5/kg (but steel requires 5x more material per mold).
- Hidden Savings: Eliminates post-machining hardening (steel molds need HRC 48–52 heat treatment).
③ Superior Cooling Efficiency
- Aluminum’s high thermal conductivity reduces cycle times by 15–25%:
- An auto parts customer produces PA66 sensor mounts with a cooling time of just 12 seconds for aluminum molds (16 seconds for steel molds), saving 1,200 hours per year for 5,000 units.
④ Design Flexibility
- Easy to modify for engineering changes (e.g., wall thickness adjustments, gate repositioning).
- Case in point: A medical startup iterated on version 3 of the design, and the aluminum mold modification cost totaled $2,100, only 10% of the steel mold.
3. When Steel Still Matters: Limitations of Aluminum
Aluminum isn’t a one-size-fits-all solution. Steel prevails in:
- High-Abrasion Scenarios: Glass-filled polymers (e.g., GF-Nylon) wear aluminum rapidly.
- Ultra-High Volumes: >50,000 shots require steel’s durability.
- Micro Features: Steel handles <0.2mm fine textures better.
4. Cost-Benefit Analysis: Aluminum’s ROI for 5,000 Units
| Expense | Aluminum Mold | Steel Mold |
| Tooling Cost | $12,000 | $40,000 |
| Per-Unit Cost* | $1.80 | $1.50 |
| Total Cost | (12,000+(5,000×1.80) = $21,000 | (40,000+(5,000×1.50) = $47,500 |
| Savings with Aluminum | $26,500 (55% lower) | / |
*Assume that the material is ABS, including machine time, labor, and energy consumption.
5. BFY Mold’s Aluminum Tooling Innovations
- Hybrid Molds: Steel inserts are embedded in key areas (e.g., gate, parting surface), and the life span is increased to 50,000+ shots.
- 3D-Printed Conformal Cooling: The aluminum mold is integrated with the shape water, increasing the cooling efficiency by 30%.
- AI-Driven Wear Monitoring: Real-time tracking of cavity wear, early warning replacement window, avoid unexpected downtime.
Customer Case:
A UAV manufacturer uses the BFY Mold aluminum + steel insert program to produce 10,000 carbon fiber reinforced PP parts, reducing mold costs by 42% and maintaining a 98% yield.
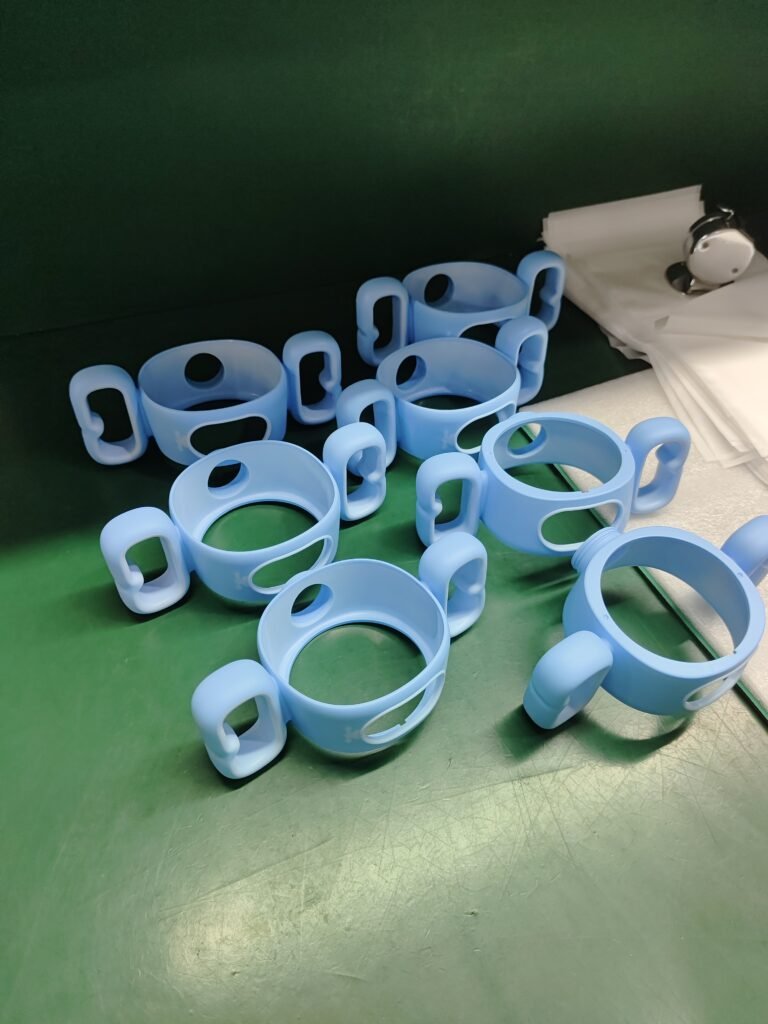

6. How to Decide on mold selection
a: Expected production?
- <10,000 pieces → Aluminum mold;>50,000 pieces →Steel molds.
b: Does the material contain abrasive filler?
- Glass fiber/carbon fiber >20% → Preferably steel mold or aluminum mold + steel inserts.
c. Is the design stable?
- Need to be modified several times → Aluminum mold flexibility and low-cost modification advantages.
Top 10 FAQs About Aluminum Molds
1. What are the key advantages of aluminum molds compared to steel molds?
Aluminum molds offer 30–50% lower costs, 2–4x faster lead times (3–6 weeks vs. 12+ weeks for steel), and lighter weight for easier handling. They are ideal for prototyping, low-volume production (50–10,000 units), and parts requiring rapid design iterations.
2. What industries commonly use aluminum molds?
- Consumer Electronics: Fast-turnaround casings for prototypes.
- Medical Devices: Low-volume production of surgical tool components.
- Automotive: Pre-production validation of interior trim parts.
3. What is the typical lifespan of an aluminum mold?
Aluminum molds last 5,000–20,000 cycles, depending on:
- Material: Abrasive resins (e.g., glass-filled nylon) reduce lifespan.
- Cooling: Efficient cooling systems extend longevity.
- Maintenance: Regular cleaning and polishing prevent wear.
4. How much does an aluminum mold cost?
Costs range from 1,500–1,500–30,000, influenced by:
- Complexity: Multi-cavity designs or side actions add 20–40%.
- Surface Finish: SPI-A1 (mirror finish) increases machining time.
- Size: Larger molds require more material and CNC hours.
5. What materials can be used?
- Plastics: ABS, PP, PC, and TPU (avoid glass-filled resins).
- Silicones: LSR for medical or food-grade applications.
- Limitations: High-temp materials (e.g., PEEK) may warp aluminum.
6. How precise are aluminum molds?
Aluminum molds achieve tolerances of ±0.05–0.1mm, suitable for most prototypes and non-critical parts. Steel molds are recommended for tighter tolerances (±0.01mm).
7. Can aluminum molds be modified for design changes?
Yes. Aluminum’s softness allows easier modifications:
- Minor changes (gate adjustments): 3–5 days, 300–300–1,000.
- Major revisions (cavity redesign): 1–2 weeks, 1,500–1,500–5,000.
8. How do I ensure quality when sourcing aluminum molds from overseas suppliers?
- Verify ISO 9001 certification and request T1 sample inspections.
- Use third-party QC services for dimensional checks (CMM reports).
- Ensure suppliers provide mold flow analysis to predict defects.
9. What maintenance is required for aluminum molds?
- Daily: Clean cavities with non-abrasive solvents.
- Weekly: Inspect and lubricate ejector pins.
- Post-Run: Polish surfaces to remove resin residue.
10. When should I transition from aluminum to steel molds?
Switch to steel when:
- Volume exceeds 10,000 units.
- Material abrasiveness demands higher durability.
- Tolerances need to be tighter than ±0.05mm.
Conclusion
“Aluminum molds offer unmatched cost and speed benefits for low-volume production. BFY Mold’s guide compares tooling costs, cycle times, and when to choose aluminum over steel. Optimize your project today.”









